Sarcosaurus is a Dinosaur that opens a window into the fascinating world of the Jurassic period, specifically the Middle Jurassic era, which existed approximately 170 million years ago. Although it is not as well-known as some other dinosaurs, its discovery and characteristics provide valuable insights into prehistoric life, habitats, and adaptations.
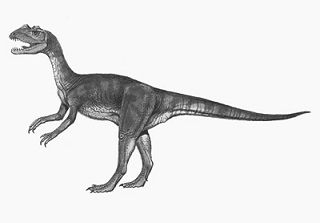
Sarcosaurus is classified as a theropod dinosaur, a group known for its bipedal stance, sharp teeth, and carnivorous diet. However, its exact placement within the theropod lineage remains a topic of debate among paleontologists due to the scarcity of fossils.
The first fossils attributed to Sarcosaurus were discovered in Scotland, hinting at its presence in what is now the United Kingdom. These remains consist of fragmentary bones, making it challenging to reconstruct the dinosaur's appearance and behavior accurately.
| Name: | Sarcosaurus dinosaurs |
| Size: | Around 6.5 to 10 feet (2 to 3 meters) in length. |
| Main Facts: | Sarcosaurus, a Late Triassic theropod, is known for its limited fossil record, making it a mysterious and enigmatic dinosaur. |
Sarcosaurus lived during the Late Triassic, a time when the Earth was undergoing significant environmental changes. The fossils found in Scotland suggest that it inhabited regions that were once part of the supercontinent Pangaea.
As a theropod, Sarcosaurus was a carnivorous predator. Its adaptations for hunting would have included keen senses, agility, and sharp teeth. It likely pursued and captured prey, possibly smaller reptiles or early mammals, in its ecosystem.
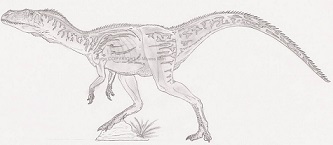
Due to the limited fossil evidence, our understanding of Sarcosaurus' physical characteristics is limited. However, certain aspects can be inferred based on its classification as a theropod :
Like all theropods, Sarcosaurus walked on two legs, which is a defining feature of this group.
Being a theropod, Sarcosaurus possessed sharp teeth designed for tearing into flesh. Its diet likely consisted of other smaller animals, making it a predator in its ecosystem.
While the exact size and build of Sarcosaurus are uncertain, it is believed to have been a relatively small theropod, possibly comparable in size to a medium-sized dog.
Sarcosaurus, a Late Triassic theropod dinosaur, is characterized by limited fossil evidence. While its exact physical attributes remain uncertain, it likely had a bipedal stance and sharp teeth suited for carnivory. Estimated to be of moderate size, similar to a medium-sized dog, its appearance and behavior are challenging to reconstruct due to fragmentary remains.
Discovered in Scotland, Sarcosaurus offers intriguing but incomplete insights into the world of early theropods during the Late Triassic, leaving many aspects of its biology and ecology shrouded in mystery.
Sarcosaurus belongs to the theropod group, sharing this classification with famous carnivorous dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex and Allosaurus. Comparisons highlight its evolutionary position within this diverse group.
Sarcosaurus was a relatively small theropod, estimated to be around 6.5 to 10 feet (2 to 3 meters) in length. Contrasting its size with larger theropods emphasizes the range of body sizes within this group.
Fossils of Sarcosaurus have been discovered in Europe, specifically in England. Comparing it to other theropods in different regions offers insights into the global distribution of these dinosaurs.
Sarcosaurus' placement within the theropod lineage and its relationships to other theropods, such as the coelophysoids, helps unravel the evolutionary connections among these predators.
Comparing Sarcosaurus' skull structure and teeth to those of other theropods reveals variations in hunting strategies, prey preferences, and adaptations.
Understanding how Sarcosaurus fit into its ecosystem, such as interactions with herbivorous dinosaurs, can be compared to the roles of other theropods in their respective environments.
Sarcosaurus lived during a time of environmental changes. Comparing its extinction to that of other Early Jurassic dinosaurs provides insights into the factors influencing dinosaur survival and decline.
While direct evidence of behavior is limited, comparing Sarcosaurus' physical features and adaptations to those of other theropods may offer clues about its hunting and social behaviors.