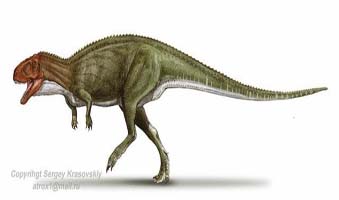
Kryptops Dinosaur is an extinct genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Upper Cretaceous Period, approximately 70 million years ago. It was a member of the Hadrosauridae family, and is the oldest known member of the clade. It was discovered in Algeria in 1997, the first dinosaur found in the country. Kryptops had a long neck and a large head.
Its skull, which was about 25 cm (10 in) long, had a wide snout and a wide lower jaw. Its teeth were small and triangular, and were used to grind vegetation. It had four short legs with five toes on each foot, and each toe had a large claw. It was a lightly built, small animal, estimated to be about 2–2.5 m (6.5–8.2 ft) in length and to weigh about 120 kg (265 lb).
Kryptops Facts :
| Name: | Kryptops Dinosaurs |
| Size: | 2-2.5 meters |
| Main Facts: | Kryptops is an extinct genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Upper Cretaceous Period, approximately 70 million years ago. |
Kryptops was a plant-eater, with the majority of its diet probably consisting of ferns and other low-growing plants that were available in its environment. Its teeth were designed to crush and grind tough plant material, not to slice through it. Its head and neck were shaped to facilitate browsing, and the shoulder joint was very flexible, allowing the animal to reach to the ground while feeding. Kryptops lived in large herds in flood plains and river valleys in North Africa. Its preferred habitat was warm and dry, with plenty of vegetation; it probably avoided cold, wet and wooded areas.
Its primary predators were theropod carnivores such as Carcharodontosaurus and Spinosaurus, which likely hunted in packs. Kryptops is important in the study of dinosaur evolution because it is the oldest known hadrosaurid, and provides evidence for the origin of that clade. It is also the first dinosaur to be discovered in the African continent, and its discovery has opened up a new field of study for paleontologists in this region. The fossils of this dinosaur are particularly well-preserved, providing valuable information about the anatomy and behavior of early hadrosaurids.