Aucasaurus is a genus of large theropod dinosaur that lived during the early Cretaceous Period, roughly 125 to 100 million years ago. It was a bipedal carnivore, measuring 6–8 metres (20–26 ft) in length, with a weight of 1.5–3 tonnes (3.3–6.6 thousand pounds). It was closely related to Allosaurus, and its fossil remains have been found in South America, mainly in Argentina. Aucasaurus was a large and powerful predator with a robust skull, large jaws filled with sharp teeth, and a large, muscular body. Its forelimbs were relatively small and its hindlimbs were long and powerful. Its tail was long and stiff and supported by a series of fused vertebrae.
Aucasaurus had an unusual feature for a theropod dinosaur: two large, curved horns that projected from the top of its head. These horns may have served a variety of purposes, such as for display or defense. Aucasaurus was an active predator, hunting other large animals, such as sauropods and ornithopods, as well as smaller creatures, such as lizards and mammals. It is thought that it may have been an ambush predator, lying in wait for its prey.
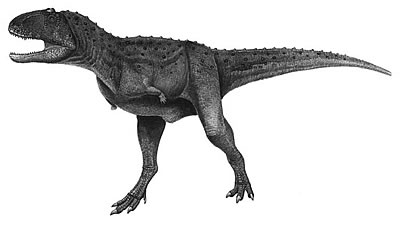
| Name: | Aucasaurus dinosaurs |
| Size: | measuring 6–8 metres (20–26 ft) in length, with a weight of 1.5–3 tonnes (3.3–6.6 thousand pounds). |
| Body: | Aucasaurus was a bipedal carnivore. |
| Skull: | Aucasaurus a robust skull. |
| Teeth : | Aucasaurus sharp teeth. |
| Main Facts: | Aucasaurus was an active predator, hunting other large animals, such as sauropods and ornithopods, as well as smaller creatures, such as lizards and mammals. It is thought that it may have been an ambush predator, lying in wait for its prey. |
Aucasaurus is a genus of abelisaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period (about 70–66 million years ago). It was discovered in 1989 in the Huincul Formation of Argentina and was named after the nearby Auca Mahuevo site where it was found. Aucasaurus was a medium-sized theropod, measuring approximately 5 meters (16.4 ft) in length. It is distinguished from other abelisaurids by its large, blunt snout and long, narrow jaws, as well as its unusually shaped, robust teeth. The teeth of Aucasaurus are unique among theropods in that the crowns are curved inward, and the tips are rounded. This form is thought to have been an adaptation for crushing shells and hard-bodied prey, suggesting that Aucasaurus was a specialized predator. Additionally, Aucasaurus is unique among abelisaurids in having short, robust forelimbs and three-fingered hands, which may have been used for grasping and manipulating prey.
Aucasaurus is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Early Cretaceous period, around 125 million to 100 million years ago. Fossils of Aucasaurus have been found in South America, primarily in Argentina and Brazil.
The first fossil remains of Aucasaurus were discovered in Argentina in 1991. These consisted of several bones including vertebrae, ribs, and limb bones. Further fossils were discovered in Argentina in 2002 and 2004. In 2005, the first partial skull of Aucasaurus was discovered in Brazil.
The fossils of Aucasaurus are well-preserved and have provided a wealth of information about its anatomy. Palaeontologists have been able to reconstruct the anatomy of this dinosaur, including its skull and teeth, body proportions, and limb structure. Other fossils have included fossilized skin impressions, scales, and claws. In addition, the discovery of fossilized eggshells in Argentina has provided evidence that Aucasaurus laid eggs.
The Aucasaurus dinosaurs are significant to today's scientific community because they represent a possible link between theropods and sauropods.
Aucasaurus was a small carnivorous dinosaur that lived during the early Cretaceous period of South America. Its fossils were first discovered in the late 19th century and were initially believed to be a species of Megalosaurus.
In the early 2000s, scientists from the University of Utah re-examined the fossils and determined that Aucasaurus was not a theropod, but instead was a basal sauropodomorph.
The significance of Aucasaurus lies in its transitional status between theropods and sauropods. Theropods are a group of dinosaurs that includes the familiar carnivorous forms such as Tyrannosaurus, while sauropods are a group of large herbivorous forms such as Apatosaurus.
Aucasaurus is the first known dinosaur to possess features of both groups, suggesting that the two major groups of dinosaurs may have evolved from a common ancestor. This has implications for our understanding of dinosaur evolution and the history of life on Earth.
the discovery of Aucasaurus has led to a better understanding of the evolution of sauropodomorphs. In particular, the analysis of its anatomy has revealed that many of the features that were previously believed to be unique to sauropods had already evolved in earlier sauropodomorphs.
This has forced scientists to re-evaluate the relationships between sauropods and theropods and has shed new light on the evolutionary history of large dinosaurs.
The discovery of Aucasaurus has also been important in terms of our understanding of the South American fossil record. Prior to its discovery, the fossil record of South America had been relatively poor, with few well-preserved specimens of dinosaurs.
The discovery of Aucasaurus has demonstrated that the region was home to a diverse array of dinosaurs during the early Cretaceous and has provided a more complete picture of the ancient environment.