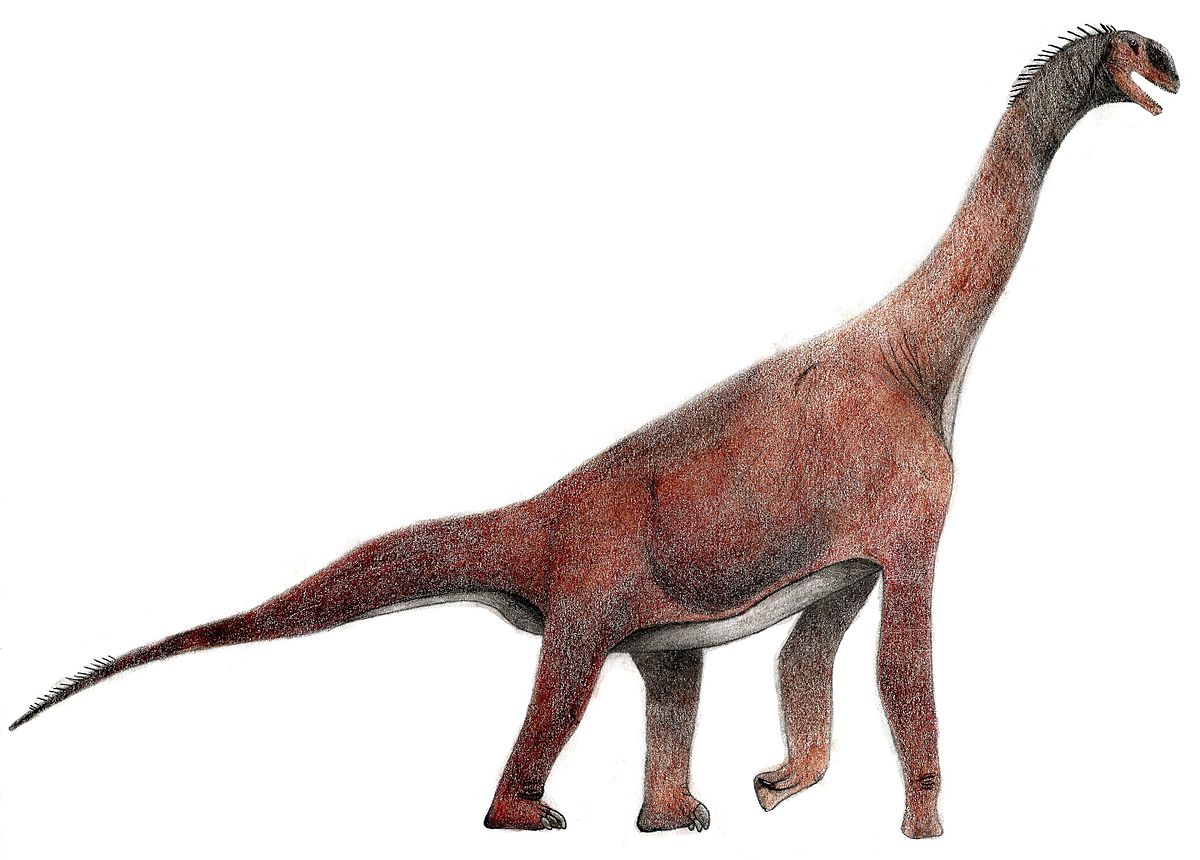
Atlasaurus is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the late Cretaceous period, around 95 million years ago. It is classified as a titanosaur, a group of sauropods characterized by their large size and unusually long neck. Atlasaurus was first discovered in the south of Morocco in the late 19th century. Its remains were discovered in the Atlas Mountains, hence the name Atlasaurus. The fossils were described in the early 20th century by French paleontologist Albert-Felix de Lapparent. Atlasaurus was a large dinosaur, estimated to have been between 18 and 25 meters long, and weighing between 10 and 15 tons. Its body shape was similar to other titanosaurians, with a long neck and body, and a relatively short tail. It had four sturdy, column-like legs, and a long, flexible neck.
Atlasaurus had a long, thick skull and beak. Its jaws were filled with numerous small, sharp teeth, which it likely used to strip leaves and other vegetation from branches. It had a large number of vertebrae in its neck and tail, suggesting that it had a large range of motion and was able to bend its neck in a variety of directions. Atlasaurus is believed to have been a herbivore, feeding primarily on leaves, fruits, and other vegetation. It likely traveled in herds, and may have been an important source of food for predators like Carcharodontosaurus and Spinosaurus.
| Name: | Atlasaurus dinosaurs |
| Size: | between 18 and 25 meters long, |
| Body: | Atlasaurus large size |
| Neck: | Atlasaurus long neck. |
| Tail : | Atlasaurus had a long tail. |
| Teeth: | Atlasaurus harp teeth. |
| Main Facts: | Atlasaurus is believed to have been a herbivore, feeding primarily on leaves, fruits, and other vegetation. It likely traveled in herds, and may have been an important source of food for predators like Carcharodontosaurus and Spinosaurus. |
Atlasaurus dinosaurs were different from other types of dinosaurs in several ways. First, they were herbivores, meaning that they ate only plants. This is different from many other dinosaur species which were carnivorous and consumed meat. Additionally, Atlasaurus dinosaurs were much smaller than other dinosaurs, with an estimated length of only about 10 feet. Furthermore, Atlasaurus dinosaurs had a unique head shape, with a flat snout and a large crest on their skull. Finally, Atlasaurus dinosaurs had a unique body shape, with a large neck and a wide rib cage.
The Atlasaurus was a large sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, around 90 million years ago. It was an herbivore, meaning it ate plants and vegetation.
It lived in the coastal region of North Africa and was adapted to living in a hot and dry climate.
The Atlasaurus was a large, quadrupedal dinosaur with a long neck and tail. Its neck and tail were both short compared to other sauropods, so it was not as tall as other dinosaurs of its kind.
Its body was well-suited for its environment, as it was able to travel long distances to find food in the dry, arid regions it inhabited.
The Atlasaurus was well-adapted to its environment because of its long neck and tail. Its long neck allowed it to reach higher leaves and branches, giving it access to more food.
Its tail was also short, which helped it move quickly through the dense vegetation of its habitat.
The Atlasaurus also had a wide girth, allowing it to store large amounts of food for later. This fat storage allowed it to survive lean times when food was scarce. Its thick, heavy skin and scales also helped protect it from the sun's rays and the extreme heat of its environment.
In order to survive in its environment, the Atlasaurus had to be able to move quickly and find food efficiently. Its long neck and tail allowed it to reach higher branches and leaves, and its wide girth allowed it to store food for later. Its thick, heavy skin and scales also helped protect it from the sun and the extreme heat of its environment.